🚀 Mastering Modern Software Delivery: Your CI/CD Pipeline Guide
Whether you’re a developer, a DevOps specialist, a tester, or involved in any modern IT role, CI/CD pipelines have become an integral part of the software development process. They are the engine that drives efficient, rapid, and reliable software delivery.
This visual guide is designed to help you grasp and enhance your methods for creating and delivering software more effectively.
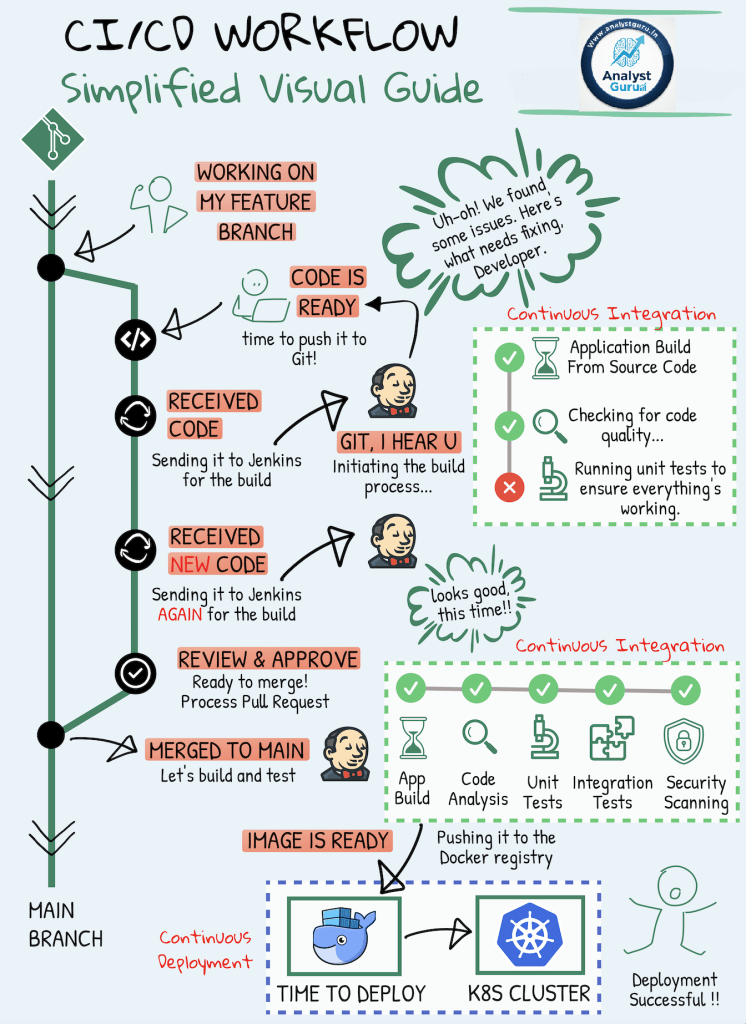
What is CI/CD? The Core Concepts
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery/Deployment. It represents a set of principles and practices that enable development teams to deliver code changes more frequently and reliably.
1. Continuous Integration (CI) 🔄
Continuous Integration (CI) is a development practice where code changes are frequently combined (integrated) into a shared central repository.
- Frequent Commits: Developers commit code changes multiple times a day.
- Automated Builds: Every commit triggers an automated build process.
- Automated Testing: The build is immediately followed by automated unit and integration tests.
- Goal: To quickly detect and address integration errors, ensuring the new code works well with the existing code base.
Think of it: CI is like making sure all the separate parts of a new car engine fit together and work before you try to put the engine into the car.
2. Continuous Deployment (CD) 📦
Continuous Deployment (CD) is the practice of automatically putting these code changes into real-world use. It extends CI by automating the release of the validated code to various environments.
CD can refer to two related concepts:
- Continuous Delivery: Ensures that every change that passes the CI stage is ready for release. The deployment to production is often a manual step triggered by a human decision.
- Continuous Deployment: Takes this a step further by automatically deploying every change that passes the full pipeline to production, with no human intervention.
- Automated Release: Code that passes all tests is automatically prepared for deployment.
- Automated Deployment: The process of moving the new code to staging, production, or other target environments is smooth and reliable.
Think of it: CD is like having an automated assembly line that not only builds the car engine (CI) but also installs it into the vehicle and drives it off the lot once it passes final quality checks.
The Power of the Pipeline 🛠️
A CI/CD pipeline is an automated workflow that connects all these practices. It’s a series of steps that a codebase goes through from the moment a developer commits a change until that change is live for users.
| Stage | Key Activities | Purpose |
| Source | Code commit/push | Initiates the pipeline on a change. |
| Build | Compile code, run static analysis | Creates a deployable artifact (e.g., a JAR file, Docker image). |
| Test | Unit tests, Integration tests, Security scans | Verifies quality and functionality. (The CI part) |
| Deploy | Deployment to Staging/Pre-Production | Tests the artifact in a production-like environment. |
| Release | Deployment to Production | Makes the new features available to end-users. (The CD part) |
✨ Benefits of Adopting CI/CD
Implementing a robust CI/CD pipeline fundamentally changes how software teams operate, leading to massive improvements:
- Faster Release Cycles: Deliver features and fixes to customers in hours or minutes, not weeks or months.
- Reduced Risk: Frequent, small deployments are inherently less risky than large, infrequent ones. Issues are isolated and easier to rollback.
- Improved Code Quality: Automated testing catches bugs early, when they are cheapest and easiest to fix.
- Better Collaboration: CI/CD encourages team members to stay in sync and share a constant, high-quality code base.
💡 Your Next Steps to CI/CD Success
Ready to enhance your delivery process?
- Start Small: If you haven’t yet, implement basic automated Unit Tests and set up an automated Build process upon commit (that’s your first CI step!).
- Choose Your Tools: Select a CI/CD platform (e.g., Jenkins, GitLab CI, GitHub Actions, CircleCI) that integrates well with your existing repository and cloud infrastructure.
- Prioritize Automation: Look for manual steps in your current release process (e.g., running tests, configuring servers) and write scripts to automate them.
CI/CD isn’t a destination; it’s a continuous journey of improvement. By mastering the pipeline, you future-proof your development process and deliver value faster than ever before.